Advantages and disadvantages of selective breeding – Selective breeding, the intentional manipulation of an organism’s genetic makeup to enhance desired traits, presents a multifaceted landscape of advantages and disadvantages. This practice has profoundly impacted agriculture, medicine, and beyond, but also raises ethical concerns and questions about genetic diversity.
In this exploration, we delve into the complexities of selective breeding, examining its potential benefits and limitations.
Selective breeding offers the ability to control desirable traits in plants and animals, resulting in improved crop yields, livestock production, and the potential to address food security and environmental challenges. However, concerns arise regarding genetic diversity, the loss of desirable traits, and the ethical implications of altering organisms’ genetic makeup.
Advantages of Selective Breeding
Selective breeding offers numerous advantages in controlling desirable traits in plants and animals. By selecting individuals with specific traits and breeding them together, breeders can improve the overall quality and performance of their populations.
Improved Crop Yields and Livestock Production
Selective breeding has significantly increased crop yields and livestock production. In agriculture, breeders have developed high-yielding varieties of crops that are resistant to pests, diseases, and adverse environmental conditions. In livestock production, selective breeding has led to animals with improved growth rates, feed efficiency, and meat quality.
Addressing Food Security and Environmental Challenges
Selective breeding can play a crucial role in addressing food security and environmental challenges. By developing crop varieties that are resistant to climate change and pests, breeders can help ensure a reliable food supply. Selective breeding can also reduce the environmental impact of agriculture by developing animals that are more efficient in converting feed into meat, reducing the need for deforestation and other environmentally damaging practices.
Disadvantages of Selective Breeding: Advantages And Disadvantages Of Selective Breeding
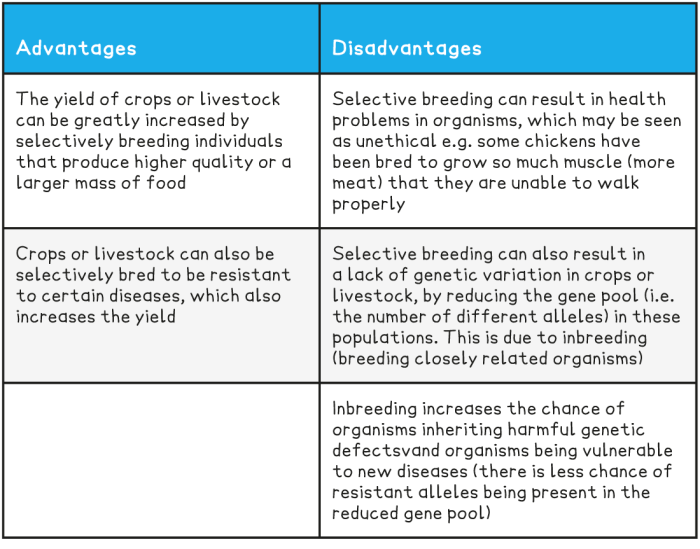
While selective breeding offers numerous advantages, it also comes with potential risks and limitations. Breeders must carefully consider these disadvantages to ensure responsible and ethical practices.
Genetic Diversity and Loss of Desirable Traits
Selective breeding can lead to a reduction in genetic diversity within a population. By focusing on specific traits, breeders may inadvertently select against other desirable traits that could be lost over time. This can make populations more vulnerable to environmental changes and diseases.
Ethical Implications
Altering the genetic makeup of organisms raises ethical concerns. Selective breeding can have unintended consequences on the health and well-being of animals and plants. Breeders must carefully consider the potential risks and benefits before making decisions about selective breeding programs.
Methods of Selective Breeding

Selective breeding is conducted using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Artificial Insemination
Artificial insemination involves the collection of semen from a desired male and inseminating females with it. This method allows breeders to control the genetic makeup of offspring and improve the quality of livestock.
Embryo Transfer, Advantages and disadvantages of selective breeding
Embryo transfer involves the collection of embryos from a desired female and implanting them into a surrogate mother. This method allows breeders to produce multiple offspring from a single high-quality female.
Applications of Selective Breeding

Selective breeding has a wide range of applications in agriculture, medicine, and other fields.
Agriculture
Selective breeding has been used to develop new varieties of crops and livestock that are more productive, resistant to pests and diseases, and better adapted to specific environmental conditions.
Medicine
Selective breeding has been used to develop animal models of human diseases, which are used to study the causes and treatments of these diseases.
Ethical Considerations
The use of selective breeding raises important ethical issues that must be carefully considered.
Responsible and Ethical Practices
Breeders must use selective breeding techniques responsibly and ethically to avoid unintended consequences. This includes considering the health and well-being of animals and plants, as well as the potential impact on genetic diversity.
Genetic Engineering and Modification of Organisms
Selective breeding can raise concerns about genetic engineering and the modification of organisms. Breeders must carefully consider the potential risks and benefits of these technologies before making decisions about their use.
Key Questions Answered
What are the primary advantages of selective breeding?
Selective breeding allows for the control and enhancement of desirable traits in plants and animals, leading to improved crop yields, livestock production, and the potential to address food security and environmental challenges.
What are the potential risks and limitations of selective breeding?
Selective breeding can lead to concerns about genetic diversity, the loss of desirable traits, and the ethical implications of altering the genetic makeup of organisms.
How is selective breeding applied in practice?
Selective breeding is used in agriculture, medicine, and other fields through methods such as artificial insemination and embryo transfer.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding selective breeding?
Selective breeding raises ethical issues related to responsible and ethical practices, as well as concerns about genetic engineering and the modification of organisms.